The fire this time?
Next time?
Are we just waiting and watching for the “big one,” knowing it is just a matter of time, or as a headline on Laurie Garrett’s story in Foreign Policy put it so succinctly last September: “The World Knows an Apocalyptic Pandemic Is Coming.”
Garrett, a former senior fellow for global health at the Council on Foreign Relations, Pulitzer Prize winning science writer, and author of the landmark 1994 book, The Coming Plague: Newly Emerging Diseases in a World Out of Balance, argued some 26 years ago now that human disruption of the global environment, coupled with behaviours that readily spread microbes between people and from animals to humans, guaranteed a global surge in epidemics, even an enormous pandemic.
How quickly we could we make a trip back to a modern-day equivalent to the Dark Ages of the 5th to 11th centuries?
Mathematician and complexity scientist John Casti’s 2012 book, X-Events: The Collapse of Everything looked at scientific modelling and prediction computer simulation as to how social “mood” can affect future trends and extreme events, sounds a clarion warning as to how easy it would be to slip suddenly into a new Dark Ages, and how the global food supply system could collapse (https://soundingsjohnbarker.wordpress.com/2015/12/12/what-if-the-22nd-century-means-staying-at-home-with-long-distance-travel-a-thing-of-the-past/). Or the “digital darkness” that would come from a widespread and prolonged failure of the internet. Or what a continent-wide electromagnetic pulse (EMG) would do to electronics, and how we may have reached peak oil in 2000, and how any of those scenarios leave us vulnerable in overly complex technological societies to an “X-event” that would send us back to a pre-modern world – and again, a world without air or other long-distance travel – virtually overnight.
New York City writer Emily St. John Mandel’s post-apocalyptic Station Eleven, her fourth novel, published in 2014, is centred around the fictional but not so implausible in the-world-after-Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV) in 2003, and the novel influenza A (H1N1) pandemic of 2009. “Georgia Flu,” is a flu pandemic so lethal, named after the former Soviet republic, that within weeks, most of the world’s population has been killed.
Station Eleven, which was a finalist for a National Book Award and the PEN/Faulkner Award, won the 2015 Arthur C. Clarke Award for best science fiction novel of the year for the British Columbia-born writer. It all begins when the character of 51-year-old Arthur Leander has a fatal heart attack while on stage performing the role of King Lear at Toronto’s Elgin Theatre.
As the novel picks up some 20 years later, “there is no more Toronto,” Sigrid Nunezsept noted in the Sept. 12, 2104 New York Times book review “Shakespeare for Survivors.” In fact, “There is no Canada, no United States. All countries and borders have vanished. There remain only scattered small towns.”
Airplanes are permanently grounded and used as cold storage facilities. There are no hospitals or clinics.
But there is the “Travelling Symphony” made up of “20 or so musicians and actors in horse-drawn wagons who roam from town-to-town in an area around the shores of Lakes Huron and Michigan,” Nunezsept writes. “At each stop the Symphony entertains the public with concerts and theatrical performances – mostly Shakespeare because, as the troupe has learned, this is what audiences prefer.”
Sadly, novel influenzas, unidentified forms of pneumonia, and other respiratory illnesses, incubating in the reservoir of wet markets, live poultry markets and farms in cities in both mainland China and Hong Kong is not a new story, but rather one that dates back at least to May 1997. The relevant questions are always the same, including how bad is it and when will we know that truth?
The Huanan Seafood Market in Wuhan is where Chinese officials believe the latest coronavirus outbreak may have originated in a wild animal sold at the food emporium, which sold live foxes, crocodiles, wolf puppies, giant salamanders, snakes, rats, peacocks, porcupines, koalas and game meats, the Daily Mail and South China Morning Post report. The market has since been closed and has been labelled ‘ground zero’ by local authorities.
We now also have time-lapse tracking of the transmission and evolution of Influenza A (H7N9), the most deadly flu on Earth, which has been circulating in China for the last five years or so. It has a mortality rate of 40 per cent, making it about 200 times more deadly than this season’s Influenza A (H3N2) flu virus circulating in Canada is expected to be. Nextstrain is an open-source project to harness the scientific and public health potential of pathogen genome data (https://nextstrain.org/flu/avian/h7n9/ha?dmax=2019-04-06&dmin=2012-03-23&fbclid=IwAR0uzebD_Fpv1UGNP3tybCf8txl3m1dpm8O7CqOkhhnXmfdQILbtQszb-bA&l=radial)
Not all pandemic news is necessarily bad news, at least in retrospect historically speaking, some academics have suggested in recent years.
In May 2014, a study in PLOS ONE, an international peer-reviewed journal, located in Levi’s Plaza (as in Levi Strauss & Co. jeans) in San Francisco, and authored by University of South Carolina anthropologist Sharon DeWitte, suggested that people who survived the medieval plague, commonly known then, as the Black Death, lived significantly longer and were healthier than people who lived before the epidemic struck in 1347. The Black Death killed tens of millions of people, an estimated 30 to 50 per cent of the European population, over just four years between 1347 and 1351, which, it turns out, may not have been such a bad thing after all (https://soundingsjohnbarker.wordpress.com/2014/09/03/black-death-not-so-bad/).
“The Black Death Actually Improved Public Health,” read the headline at the Smithsonian, the official journal published by the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C. When it comes to science, you don’t get much more prestigious than the Smithsonian. On the more populist end of the online spectrum, AOL Inc., based in nearby Dulles, Virginia, went with “Black Death may have improved European health” on its AOL.com website.
DeWitte’s study of the Black Death suggested it was not an indiscriminate killer, but instead targeted frail people of all ages and that survivors experienced improvements in health and longevity, with many people afterwards living to ages of 70 or 80 years old. While improvements in survival post-Black Death didn’t necessarily equate to good health over a lifespan, it did demonstrate a hardiness to endure disease, either directly or indirectly, powerfully shaped mortality patterns for generations after the epidemic ended, she argues.
The skeletal samples for DeWitte’s study came from medieval London cemeteries and are curated at the Museum of London Centre for Human Bioarchaeology.
The pre-Black Death samples came from St. Mary Spital, Guildhall Yard and St. Nicholas Shambles, dating to the 11th and 12th centuries, based on stratigraphic and documentary data and artifacts. The post-Black Death samples came from the cemetery associated with the Cistercian Abbey of St. Mary Graces, which was established in London in 1350, as the Black Death was about to end, and it was in use until the Protestant Reformation in 1538.
As it happens, I find the particular subject of La moria grandissima fascinating. Way back on July 14, 2008, I fired off an e-mail to Sheena Spear at the Thompson Public Library, trying to borrow a copy of John Hatcher’s The Black Death: An Intimate History of the Plague on inter-library loan. Alas, as it had just been published a month earlier in June 2008, that wasn’t happening.
But on Oct. 13, 2011, Megan O’Brien was able to tell me she could bring in on inter-library loan a copy of The Great Mortality: An Intimate History of the Black Death, the Most Devastating Plague Of All Time by John Kelly, published in 2005. Good enough.
The Black Death swept across Europe, killing a third of the population. As Kelly, and others have pointed out, it proved a major challenge to the Church, striking down both believers and non-believers alike, testing religious faith. If anything priests were at higher risk than most, as they were called onto minister to those gravely ill.
Infected rats aboard Genoese sailing ships piloted by Italian sailors, returning from the Far East and docking in Sicily, carried fleas that spread the disease when they bit humans. Think Ground Zero.
The plague is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Pneumonic plague is characterized by lung infection and spitting blood and occurs when Y. pestis infects the lungs. This type of airborne plague can spread from person-to-person through the air. Transmission can take place if someone breathes in aerosolized bacteria.
Bubonic plague is characterized by swollen lymph glands, known as buboes, a type of boil, and is the most common form of plague. It occurs when an infected flea bites a person or when materials contaminated with Y. pestis enter through a break in a person’s skin. Patients develop swollen, tender lymph glands, called buboes, and fever, headache, chills, and weakness. Bubonic plague does not spread from person to person.
A third type of plague, septicemic plague occurs when plague bacteria multiply in the blood. It does not spread from person-to-person.
Novel influenza A(H1N1) hit parts of Northern Manitoba hard in 2009, especially south of Thompson, in places like the Island Lake First Nations of Wasagamack, St. Theresa Point, Red Sucker Lake and Garden Hill.
The novel H1N1 influenza pandemic, which started in Mexico in March 2009, albeit with relatively mild symptoms in most cases, was the first pandemic since the Hong Kong Flu of 1968. It originated in Guangdong Province in southeast China, but the first record of the outbreak was in Hong Kong on July 13, 1968.
By the end of July, extensive outbreaks were reported in Vietnam and Singapore. By September 1968, Hong Kong Flu reached India, Philippines, northern Australia and Europe. That same month, the virus entered California via returning Vietnam War troops but did not become widespread in North America until December 1968.
A vaccine became available in 1969 one month after the Hong Kong flu pandemic peaked in North America. About a million people died worldwide in what are described as “excess” death beyond what be expected in a normal flu season, but still only half the mortality rate of the Asian flu a decade earlier. H1N1 swine flu is the first worldwide influenza pandemic since the Hong Flu of 1968-69.
A decade earlier, the Asian Flu pandemic of 1957 was an outbreak of avian-origin H2N2 influenza that originated in China in early 1956 and lasted until 1958. It originated from mutation in wild ducks combining with a pre-existing human strain. The virus was first identified in Guizhou and spread to Singapore in February 1957, reaching Hong Kong by April and the United States and Canada by June 1957. Estimates of worldwide deaths caused by the Asian Flu pandemic vary, but the World Health Organization believes it is about two million.
The Asian Flu strain later mutated through antigenic drift into H3N2, resulting in the milder Hong Kong Flu pandemic of 1968 and 1969.
Three subtypes of haemagglutinin (H1, H2 and H3) and two subtypes of neuraminidase (N1 and N2) are recognized among influenza A viruses that have caused widespread human disease, says the Public Health Agency of Canada. “Since 1977 the human H3N2 and human H1N1 influenza A subtypes have contributed to influenza illness to varying degrees each year.”
Influenza B viruses have evolved into two antigenically distinct lineages since the mid-1980s, represented by B/Yamagata/16/88-like and B/Victoria/2/87-like viruses. Viruses of the B/Yamagata lineage accounted for the majority of isolates in most countries between 1990 and 2001. Viruses belonging to the B/Victoria lineage were not identified outside of Asia between 1991 and 2001, but in March 2001 they re-emerged for the first time in a decade in North America. Since then, viruses from both the B/Yamagata and B/Victoria lineages have variously contributed to influenza illness each year.
In Canada, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) reports:
- Influenza A(H3N2), A(H1N1) and B continue to co-circulate;
- Influenza A remains the predominant circulating type and influenza B continues to circulate at higher levels than usual;
- A(H1N1) and A(H3N2) are circulating in almost equal proportions. For the season to date, there is a slight majority (53 per cent) of A(H1N1), due to an increase in detections in recent weeks;
- The highest cumulative hospitalization rates are among children under five years of age and adults 65 years of age and older.
Although influenza A remains the predominant laboratory-confirmed circulating type, influenza B continues to circulate at higher levels than usual. In addition, while A(H3N2) remains the predominant subtype for the season to date, the proportion of A(H1N1) appears to be increasing.
Differences in the predominant circulating type/subtype by age-group are observed. The majority (90 per cent) of sentinel site hospitalizations among adults are associated with influenza A, while pediatric sentinel hospitalizations are a mix of influenza A (46 per cent and B (54 per cent).
Influenza A viruses are classified into subtypes based on two surface proteins: haemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA).
Of these, the influenza A viruses that have caused widespread human disease over the decades are:
Three subtypes of HA (H1, H2 and H3)
Two subtypes of NA (N1 and N2)
Influenza B has evolved into two lineages:
B/Yamagata/16/88-like viruses
B/Victoria/2/87-like viruses
Over time, antigenic variation (antigenic drift) of strains occurs within an influenza A subtype or B lineage. The ever-present possibility of antigenic drift requires seasonal influenza vaccines to be reformulated annually. Antigenic drift may occur in one or more influenza virus strains.
The global mortality rate from the 1918/1919 “Spanish Flu” pandemic is not known, but it is estimated that 10 to 20 per cent of those who were infected died.
2019-nCoV is a novel coronavirus, the first such outbreak in eight years.
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV), was first reported in Saudi Arabia, but later retrospectively identified and traced to the first known index case of MERS-CoV having occurred on the Arabian Peninsula in Jordan in April 2012; most people infected developed severe respiratory illness, including fever, cough, and shortness of breath. About three or four of every 10 patients reported with MERS-CoV died, a 30 to 40 per cent mortality rate.
Almost 10 years earlier, in November 2002, the first known case of an atypical pneumonia, later identified as Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS–CoV) occurred in Foshan City, Guangdong Province, China. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a total of 8,098 people worldwide became sick with SARS during the 2002-2003 outbreak. Of these, 774 died. Since 2004, there have not been any known cases of SARS reported anywhere in the world, but on Oct. 5, 2012, the Federal Select Agent Program, a national registry program jointly comprised of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Division of Select Agents and Toxins, and the Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service/Agriculture Select Agent Services, published a final rule declaring SARS coronavirus a select agent. A select agent is a bacterium, virus or toxin that has the potential to pose a severe threat to public health and safety. The program oversees the possession, use and transfer of biological select agents and toxins, which have the potential to pose a severe threat to public, animal or plant health or to animal or plant products.
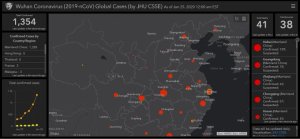
2019-nCoV, which shows signs of being far worse than SARS-CoV, has resulted in lockdowns today in two Chinese cities, Wuhan and Huanggang.
Yi Guan, a Chinese virologist, who played an important role in tracing the development of SARS-CoV, said, “I’ve experienced so much and I’ve never felt scared before. But this time I’m scared,” Nathan Vanderklippe, Asia correspondent for the Globe and Mail, and Alexandra Li, in Beijing, reported today.
“’Conservative estimates suggest that the scale of infection may eventually be 10 times higher than SARS,’ said Dr. Guan, director of the State Key Laboratory of Emerging Infectious Diseases at the University of Hong Kong, told China’s Caixin media group on Thursday,” the Toronto-based paper reported. Dr. Guan spent two days in Wuhan this week.
2019-nCoV was first detected last month in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China, and the virus did not match any other known virus. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention describes it as “an emerging, rapidly evolving situation.” Elizabeth Cohen, CNN’s senior medical correspondent, reports that a single patient, what’s called a “super spreader” or “super shredder,” has infected 14 health care workers (https://www.cnn.com/2020/01/23/health/wuhan-virus-super-spreader/index.html?).
The Geneva-based World Health Organization said earlier today that “now is not the time” to call a global health emergency related to a new coronavirus that has left 17 dead and more than 500 others infected in China, according to reports from the Associated Press, CTV News Channel, and other media.
The World Health Organization made the announcement in Geneva at a press conference after the second meeting this week of a WHO emergency advisory committee on the new virus.
It was “a bit too early to consider that this event is a public health emergency of international concern,” said Didier Houssin, the chair of the emergency advisory committee, noting that there remained strong divisions during discussions.
“The emergency committee members were very divided, almost 50-50,” he said. Some felt the severity of the disease and increase in cases warranted a global health emergency, he added.
“Several others say that it is too early because of limited number of cases abroad and also considering the efforts which are presently made by Chinese authorities in order to try to contain the disease,” he continued. “Declaring a public health emergency of international concern is an important step in the history of an epidemic.”
A “public health emergency of international concern” (PHEIC) must be an “extraordinary event” that poses a global risk and requires co-ordinated international action, according to WHO. Global emergencies have been declared before, including for the Zika virus outbreak in the Americas, the swine flu and polio.
Key to the announcement were recent extraordinary precautions already in place around China. Beijing announced it would cancel public celebrations of Lunar New Year, which is typically one of the busiest travel seasons of the year.
“They’re making a very concerted effort in China to try and contain things. We’re making efforts worldwide. That’s the most important thing,” said Susy Hota, the medical director of Infection Prevention and Control at the University Health Network in Toronto, on CTV News Channel. The committee was likely attempting to strike a “balance” to avoid negative consequences, Hota added.
Global health emergencies often prompt foreign governments to restrict travel and trade to affected countries. In 2003, WHO issued travel warnings for Toronto during the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), which impacted the Greater Toronto Area economy at the time. Hotels in the area lost $39 million in revenue in one month, according to the Canadian Tourism Commission.
“It would be very similar for China,” said infectious disease physician Michael Gardam on CTV’s Your Morning. “People would definitely avoid the country.”
There are still a number of “unknowns” to be probed, the WHO said at the Thursday press conference, including the possible animal source of the virus, its mode of transmission and the quality of containment measures.
The WHO announcement was encouraging for Neil Rau, an infectious disease specialist and assistant professor at the University of Toronto.
“If they had said it was an emergency, it would mean they were more concerned,” he said, adding that the announcement underscored the fact that the committee still needs more information on two key things:
First, how deadly is the virus? “What percentage of people who get this infection actually die from it? Based on my calculations it looks like it’s only about two per cent.”
Second, how contagious is the virus? “It’s looking right now that there are no chains of transmission beyond what we call a secondary chain,” he said. “In other words, a person has it, then a person in close contact with them gets it, but it doesn’t keep transmitting person-to-person after that.”
The committee added Thursday that they would be prepared to convene again “as soon as necessary” as more information emerges.
A global health emergency likely would not have changed much in Canada, according to Gardam, much in thanks to 17 years of preparation for another outbreak after SARS.
“We learned a lot from SARS. We also went through the H1N1 pandemic in 2009. So there’s been a lot of preparation done quietly in the background,” he said.
In Canada, travellers from Wuhan are screened, others are put in isolation who have symptoms, and hospitals have stockpiled necessary equipment for an outbreak. Those procedures would continue, said Gardam. It’s possible that a broader screening process to include travellers from Beijing or China in general may be implemented, he added. But that is less about the declaration from WHO, and more about where the virus is linked to in China.
“We may start to broaden our screening criteria. As we do that, we’re going to start screening a lot more people,” he said.
On the ground, that process would have a major impact for health care workers. “That’s going to be quite disruptive for the running of our hospitals,” he said. “We’re already pretty full dealing with all the other respiratory viruses.”
You can also follow me on Twitter at: https://twitter.com/jwbarker22


 While some 675,000 Americans died over three years between January 1918 and December 1920 during the three waves of the Spanish Flu pandemic, the country’s population was 103.2 million. Today, the population of the United States is more than 331 million. The world population in 1918 was about 1.8 billion, compared to about 7.8 billion people today.
While some 675,000 Americans died over three years between January 1918 and December 1920 during the three waves of the Spanish Flu pandemic, the country’s population was 103.2 million. Today, the population of the United States is more than 331 million. The world population in 1918 was about 1.8 billion, compared to about 7.8 billion people today.
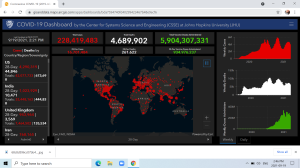
 The rolling real time daily death count on the online COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU) in Baltimore functions as our equivalent of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists’ “Doomsday Clock,” circa 1947, and the clock itself, set at 100 seconds before midnight last Jan. 27, is being profoundly influenced by COVID-19.
The rolling real time daily death count on the online COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU) in Baltimore functions as our equivalent of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists’ “Doomsday Clock,” circa 1947, and the clock itself, set at 100 seconds before midnight last Jan. 27, is being profoundly influenced by COVID-19.

















 The problem with sports being a metaphor for life is not that the claim is inaccurate: sports truly is a metaphor for life. The problem is the terrain of what constitutes a metaphor for life is a vast landscape. Within sports, virtually everything can and is described as being a metaphor for life.
The problem with sports being a metaphor for life is not that the claim is inaccurate: sports truly is a metaphor for life. The problem is the terrain of what constitutes a metaphor for life is a vast landscape. Within sports, virtually everything can and is described as being a metaphor for life.